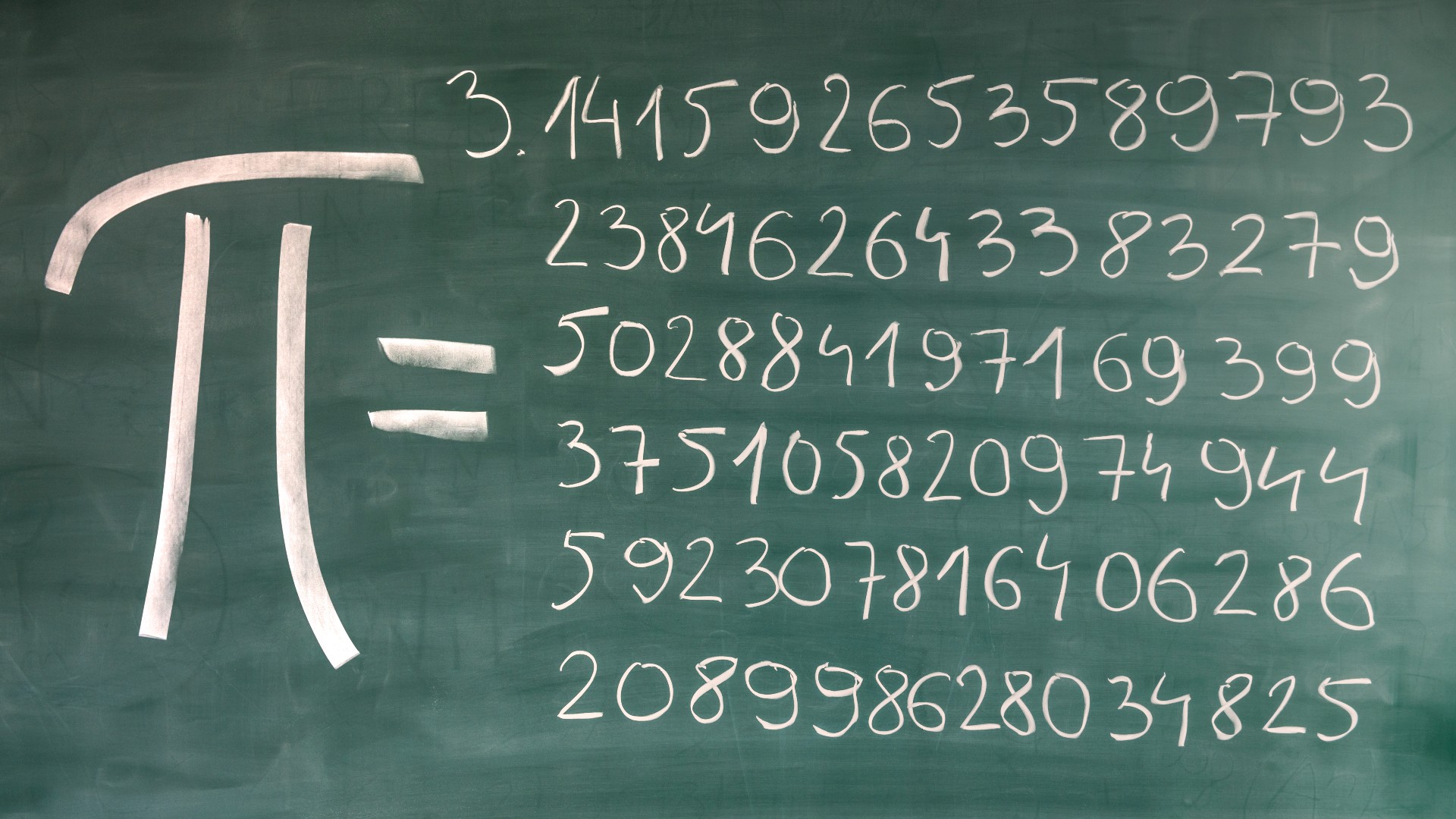
Pi (π) is one of the most important and well-known constants in mathematics. It represents the ratio between a circle’s circumference and diameter. No matter the size of the circle, this ratio is always the same:
\[ \pi = \frac{\text{Circumference}}{\text{Diameter}} \approx 3.14159 \]
This value never changes — it’s a universal constant used in geometry, engineering, science, and more.
Where is Pi Used?
1. In Geometry and Measurement
- Area of a circle: \[ A = \pi r^2 \]
- Circumference of a circle: \[ C = 2\pi r \]
- Volume of a cylinder: \[ V = \pi r^2 h \]
Halimbawa:
Kapag ang tubero ay nag-iinstall ng malaking tangke ng tubig, ginagamit nila ang formula ng volume ng cylinder para malaman kung gaano karami ang kayang lamanin ng tangke.
2. In Everyday Life
Halimbawa:
Kung may gulong ng kariton na kailangang sukatin kung ilang ikot ang kailangan para makalakad ng 10 metro, ginagamit ang formula ng circumference para makuha ito.
Halimbawa:
Kapag naghahati ng pizza, at gusto mong pantay ang bawat slice, ginagamit ang konsepto ng arc at angle — mga ideya sa math na may kinalaman kay π.
Pi Is an Irrational Number
Pi is not a fraction and it can’t be written as an exact decimal — its digits go on forever without repeating. It starts like this:
\[ \pi = 3.1415926535\ldots \]
Because of this, we usually use approximations like 3.14 or 22/7 when solving basic problems.
Sample Problem
Problem:
A circular table has a radius of 3 feet. What is its area?
Solution:
\[ A = \pi r^2 = \pi (3)^2 = 9\pi \approx 28.27 \text{ square feet} \]
So, the surface of the table is approximately 28.27 square feet.
Summary
Pi is essential when working with circles, cylinders, or anything round. It’s a constant that helps us measure space, build machines, and understand the shapes around us.
Kahit nasa eskwelahan ka o sa bahay lang, kapag may bagay na bilog — plato, takip ng kaldero, o gulong ng bisikleta — siguradong may math na gamit sa likod niyan. At kasama diyan si π.